Lost foam casting (EPC), also known as full-mold casting, is a casting process that uses an expendable foam pattern to create complex and near-net-shape castings. It offers advantages such as high dimensional accuracy, design flexibility, and reduced machining costs compared to traditional sand casting.
Here are the key specifications, requirements, and safety precautions for the lost foam casting process:
I. Key Specifications and Requirements
1. Pattern Materials and Quality:
- Polystyrene (EPS)is the most common material for foam patterns due to its low cost, ease of processing, and complete vaporization during pouring.
- Other foam materialssuch as STMMA (styrene-methyl methacrylate copolymer) or EPMMA (ethylene-propylene-methyl methacrylate terpolymer) can also be used.
- The quality of the foam patternsignificantly affects the casting accuracy and surface finish. Patterns should have uniform density, be free from defects, and properly dried before coating application.
2. Coating Systems:

Refractory coatings are crucial in lost foam casting as they:
Support and protect the foam pattern.
Prevent molten metal infiltration into the sand, preventing sand adhesion.
Facilitate the smooth escape of decomposition gases.
Maintain the integrity of the mold cavity.
Coating properties that are essential for successful casting include:
High strength and rigidity.
High refractoriness.
Excellent permeability.
Strong adhesion.
Good applicability.
Good sintering and peelability.
Common refractory materials used in lost foam casting coatings include:
Zirconium silicate: offers high fire resistance and excellent anti-sand sticking properties, suitable for casting steel and large cast iron parts.
Quartz powder: commonly used for casting small iron, aluminum, and copper parts.
Alumina: a high-performance refractory material often used for steel and large cast iron parts.
Graphite powder: widely used in cast iron production due to its high fire resistance but is prone to oxidation.
Kyanite: decomposes into mullite at high temperatures, making it a suitable substitute for alumina-based materials.
3. Molding Sand:
- Dry silica sandis typically used in lost foam casting.
- The sand should have high silica content (85%-90% or more), appropriate particle size distribution (0.850–0.300 mm for steel and iron castings), good permeability, and refractoriness.
4. Pouring System Design:
- The gating systemplays a vital role in ensuring the smooth flow of molten metal and the successful evacuation of decomposition gases.
- The design of the pouring system in EPCdiffers from traditional sand casting and should consider the specific characteristics of the process.
- Factors to considerwhen designing the pouring system include:
Casting size and shape.
Model cluster configuration.
Pouring temperature.
Metal flow resistance due to the vaporizing pattern.
The necessity of using a closed pouring system to maintain pouring stability.
5. Pouring Temperature Control:
- The pouring temperature in EPCshould be slightly higher (30-50°C) than in traditional sand casting to compensate for the heat absorbed during foam vaporization.
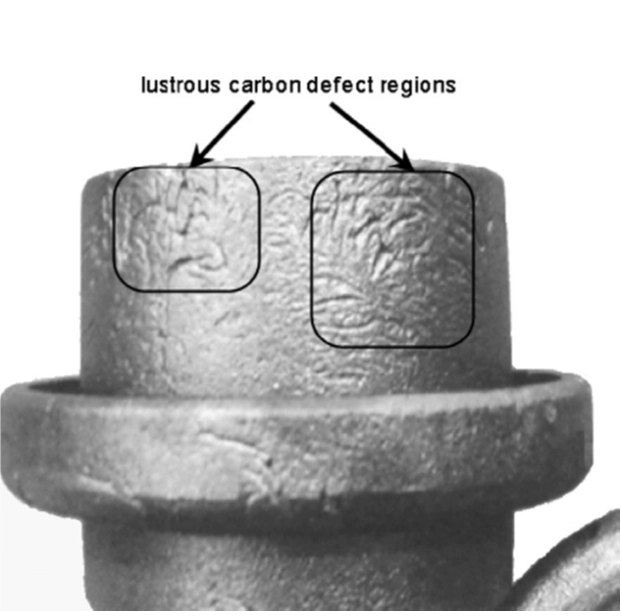
- Insufficient pouring temperaturecan lead to defects like incomplete filling, cold shuts, and wrinkles.
- Excessively high temperaturescan cause sand inclusion defects.
6. Negative Pressure Control:
- Negative pressureis a crucial aspect of EPC, especially for black alloys (iron and steel), as it helps:
Increase the strength and rigidity of the sand mold.
Efficiently remove the gaseous products generated from pattern decomposition.
- The level of negative pressureand its holding time are determined by factors such as:
Casting material.
Model cluster structure.
Coating type and thickness.
Casting size.
7. Vibration Compaction:
- Vibration compaction of the sand moldis essential for achieving:
Proper packing density of the sand.
Uniform support for the foam pattern.
Prevention of casting defects caused by mold deformation or coating cracking.
- Vibration parameterssuch as excitation force, amplitude, and vibration time should be carefully adjusted to prevent pattern deformation.
II. Safety Precautions
1. Molten Metal Handling:
- Molten metal handling involves inherent risks, and appropriate safety procedures and personal protective equipment (PPE)should be strictly followed.
- PPE should include heat-resistant clothing, gloves, face shields, and safety shoes.
- Proper ventilation and exhaust systemsare essential to control fumes and gases generated during the melting and pouring processes.
2. Pattern and Coating Material Handling:
- Some foam pattern materials and coating components can release harmful fumesduring processing or decomposition.
- Adequate ventilationis necessary when handling these materials.
- Safety data sheets (SDS)for all materials should be readily available and consulted for safe handling procedures.
3. Sand Handling:
- Dry silica sand can generate dustduring handling, which can pose respiratory hazards.
- Dust suppression measuressuch as wetting the sand or using local ventilation systems should be employed.
- Respiratory protectionlike dust masks should be worn when handling dry sand.
4. Fire Hazards:
- The presence of flammable materials like foam patterns and combustible decomposition products poses fire hazards.
- Fire prevention measuressuch as proper storage of flammable materials, availability of fire extinguishers, and clear evacuation procedures are crucial.
5. Preventing Splashing during Pouring:
- Molten metal splashingcan cause severe burns and other injuries.
- Measures to prevent splashing include:
Using low-density foam patterns.
Thoroughly drying the foam patterns before coating.
Avoiding coating the direct and lateral pouring channels.
Installing a baffle plate above the pouring cup to deflect splashes.
Company Overview: Hangzhou Ouchen Technology Co., LTD
Hangzhou Ouchen Technology Co., LTD, based in Xindeng Town, Fuyang District, is a leading manufacturer specializing in high-end intelligent lost foam casting equipment. The company integrates advanced German EPS/EPP technology with its own innovations. Ouchen is recognized as a crucial partner in the China Lost Mold Industry Association, holding titles like “National High-Tech Enterprise,” and is committed to delivering innovative and quality solutions.

Ouchen offers a range of advanced lost foam casting machines:
Foam Pattern Production Machines:
- Foam Sheet Machine: Creates foam sheets for patterns with reliable controls.
- Pre-Foaming Machines: Expands EPS beads, available in Bottom Dischargeand Fully Automatic models with precise control for minimal bead expansion deviation.
- Maturation Silo: A computer-controlled system for storing and stabilizing pre-expanded beads, ensuring consistency.
- Foam Molding Machines: Includes Verticaland Horizontal models with automated operations and robust designs for improved efficiency.
Essential Lost Foam Casting Auxiliary Equipment:
- Air Dryer: Offers energy-efficient, environmentally friendly drying options.
- Central Vacuum System: Ensures a clean, dust-free environment.
- Lift Type Paint Mixer: Ensures consistent coating quality.
Ouchen’s equipment is built with cutting-edge technology, maximizing energy savings and performance, with comprehensive after-sales support.
Conclusion
Lost foam casting is a versatile process that delivers high-dimensional accuracy and complex designs. However, its success relies on adhering to strict specifications, precise process control, and robust safety measures. By understanding these aspects, manufacturers can leverage the benefits of EPC while ensuring safe and high-quality production.
Note: This response is based solely on the provided sources and may not encompass all aspects of lost foam casting. Consult industry standards, best practices, and expert advice for comprehensive information and guidance.